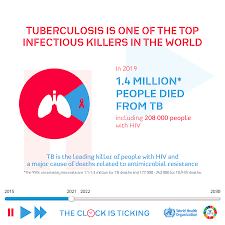
Each year approximately 10 million people fall ill with TB globally and 1.4 million people lose their lives from Tuberculosis, a preventable and curable disease. This is because many of those at the highest risk of tuberculosis have little to no access to health care. Thus, Tuberculosis remains one of the world’s top infectious killers. Nearly 4000 lives are lost to Tuberculosis and close to 28,000 people fall ill with this preventable and curable disease every day.
The World Health Organization set aside March 24 every year to raise public awareness about the devastating health, social and economic consequences of Tuberculosis, and to step up efforts to end the global TB epidemic— World Tuberculosis Day. This theme, ‘The Clock is Ticking’, conveys the message that we are running out of time to put an end to increasing new TB infection and progression while reducing the risk of mortality to already infected. This is in line with WHO’s action towards Universal Health Coverage.
What is Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a bacteria that most often affect the lungs. Tuberculosis is curable and preventable.
How is Tuberculosis spread?
TB is spread from person to person through the air. When people with lung TB cough, sneeze or spit, they propel the TB germs into the air. A person needs to inhale only a few of these germs to become infected. About a quarter of the world’s population has a TB infection. This means people have been infected by TB bacteria but are not yet ill with the disease and cannot transmit it.
Who is most at risk?
Tuberculosis mostly affects adults in their most productive years. However, all age groups are at risk. Over 95% of cases and deaths are in developing countries.
Those with HIV infection and other immunosuppressive conditions
Malnourished/ Undernourished people
Alcoholics
Smokers
Intravenous drug abusers
Diabetes mellitus
Immunosuppressive therapy
End-stage renal disease
Age below 5 years

Signs and Symptoms
Classic clinical features associated with active pulmonary TB are:
Cough
Weight loss/ loss of appetite
Fever
Night sweats
Hemoptysis( presence of blood in cough)
Chest pain
Fatigue/ Tiredness
Diagnosis:
Screening methods for TB include:
Mantoux tuberculin skin test
Acid-fast bacilli (AFB) smear and culture using sputum obtained from the patient

How can TB infection be prevented?
TB preventive treatment stops TB infection from progressing to disease in those who are infected and can protect both the individual and the community from TB.
BCG vaccination
BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guérin) is a live vaccine against tuberculosis prepared from a strain of a weakened bovine tuberculosis bacteria. It is currently the only licensed vaccine against TB and has been in use since 1921. It is one of the most widely used vaccines worldwide, however, its effectiveness is limited.
Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment is the most effective way to prevent the spread of tuberculosis. A person with infectious tuberculosis can infect up to 10–15 other people per year. But once diagnosed with TB, and started on treatment, the majority of patients are no longer infectious after just two weeks of taking the medication.

Managing Your Environment
TB is an airborne infection. The bacteria are released into the air when someone with infectious TB coughs or sneezes. The risk of infection can be reduced by:
~Good ventilation
~Good hygiene
~Use of protective masks especially in healthcare settings.
~Isolation of potentially infectious patients separate from other patients
~Regular screening of healthcare workers for TB.
A Healthy Immune System
Having a healthy immune system is the best form of defence against TB. 60% of adults with a healthy immune system can completely kill TB bacteria. Hence, good nutrition and stopping dangerous lifestyles like smoking, intravenous drug use and alcoholism can build a healthy immune system.
Treatment
TB is a treatable and curable disease. Active, drug-susceptible TB disease is treated with a standard 6-month course of 4 antimicrobial drugs that are provided with information and support to the patient by a health worker or trained volunteer. Without such support, treatment adherence is more difficult.
Since 2000, an estimated 63 million lives were saved through TB diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion:
As we commemorate yet another World TB day, let us remember the clock is ticking, we are running out of time. We must ensure healthy lifestyles and carry out regular screening for the risk population because early detection leads to early treatment and reduction of spread.
Spread the news, not the bacteria!